Proper Storage: How to Store Fruits, Vegetables, and Meats Correctly
Proper storage of fruits, vegetables, and meats is essential for maintaining their nutritional value and preventing foodborne illnesses. Storing them correctly can also help reduce food waste, saving you money and reducing your environmental impact. In this article, we will provide you with some tips on how to store your produce and meats correctly to keep them fresh for as long as possible.
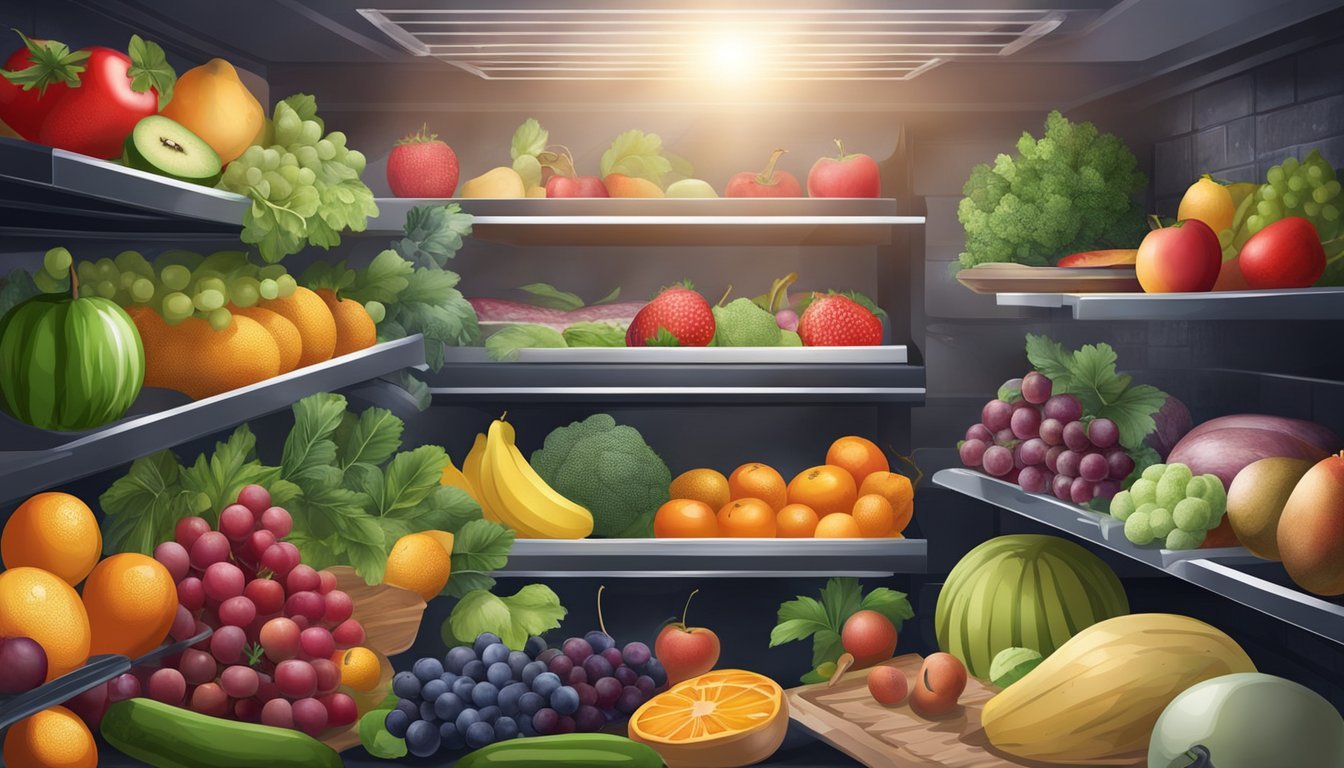
When it comes to storing fruits and vegetables, there are a few general rules to follow. First, it’s important to keep them dry, as moisture can cause them to spoil more quickly. Second, you should store them in the right temperature and humidity conditions, as different fruits and vegetables have different requirements. Finally, it’s important to store them separately, as some fruits and vegetables release ethylene gas, which can cause others to ripen and spoil more quickly.
Meat storage is also important to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses. Proper storage of meat involves keeping it at the right temperature, separating it from other foods, and storing it in the correct place in your refrigerator or freezer. By following these tips, you can ensure that your food stays fresh and safe to eat.
Fundamentals of Food Storage
When it comes to food storage, there are three fundamental factors to consider: temperature control, humidity management, and separation and contamination prevention. Proper execution of these factors can help extend the shelf life of your food and reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
Temperature Control
Temperature control is essential in food storage. Different types of food require different temperature ranges to maintain their freshness and quality. For example, perishable foods like meat, dairy, and eggs need to be kept at refrigerator or freezer temperatures to prevent bacterial growth and spoilage. On the other hand, non-perishable foods like canned goods and dry goods can be stored at room temperature.
It’s important to note that even within the same category of food, different types may require different temperature ranges. For instance, fruits and vegetables have varying temperature requirements depending on their type and ripeness. As a general rule, fresh produce should be stored at temperatures between 32°F and 40°F (0°C and 4°C) to slow down the ripening process and prevent premature spoilage.
Humidity Management
Humidity management is another crucial factor in food storage. Some foods, such as leafy greens, berries, and herbs, are highly sensitive to moisture and can wilt or rot quickly if stored in a humid environment. On the other hand, other foods, such as root vegetables and fruits, require a certain level of humidity to maintain their freshness and prevent them from drying out.
To manage humidity levels, you can use different storage methods and containers. For example, you can store leafy greens in airtight containers with a paper towel to absorb excess moisture. Alternatively, you can use perforated bags or containers for fruits and vegetables that require higher humidity levels.
Separation and Contamination Prevention
Separation and contamination prevention are critical in food storage to avoid cross-contamination and the spread of harmful bacteria. Raw meat, poultry, and seafood should always be stored separately from other foods to prevent the transfer of bacteria. You should also use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination.
In addition, you should always practice proper food handling and storage techniques to prevent contamination. This includes washing your hands and surfaces frequently, storing food in clean and airtight containers, and checking expiration dates regularly.
By following these fundamental principles of food storage, you can ensure that your food stays fresh, safe, and delicious for longer periods.
Specific Storage Techniques
Fruits: Ethylene Producers and Sensitive Varieties
When it comes to storing fruits, there are two main categories to consider: ethylene producers and ethylene-sensitive varieties. Ethylene is a natural gas that fruits produce as they ripen. Ethylene producers like apples, bananas, and avocados should be stored separately from ethylene-sensitive varieties like berries, grapes, and leafy greens. This will prevent the ethylene from the producers from speeding up the ripening process of the sensitive fruits.
To store your fruits properly, keep them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. You can also store them in the refrigerator, but be sure to keep ethylene producers and sensitive varieties separate. For example, store apples and bananas in one drawer and berries and leafy greens in another.
Vegetables: Root, Leafy, and Cruciferous
Vegetables can be divided into three categories: root vegetables, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower. Each category has different storage requirements.
Root vegetables like carrots and potatoes should be stored in a cool, dark place with good ventilation. A root cellar or pantry is ideal. Keep them away from fruits, as the ethylene produced by the fruits can cause the vegetables to spoil faster.
Leafy greens like lettuce and spinach should be stored in the refrigerator, either in a plastic bag or wrapped in a damp paper towel. This will help prevent them from drying out and wilting.
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower should also be stored in the refrigerator, but in a different drawer than your leafy greens. They can be stored for up to a week, but be sure to use them before they start to turn yellow or develop brown spots.
Meats: Red, Poultry, and Seafood
When it comes to storing meats, it’s important to follow food safety guidelines to prevent foodborne illness. Raw meat should always be stored on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator to prevent any juices from dripping onto other foods. It should also be kept in its original packaging until you’re ready to use it.
Red meat can be stored in the refrigerator for up to five days, while poultry should be used within two days. Seafood is more perishable and should be used within one to two days. If you’re not going to use the meat right away, you can freeze it for later use. Be sure to wrap it tightly in plastic wrap or aluminum foil and label it with the date before storing it in the freezer.
By following these specific storage techniques, you can ensure that your fruits, vegetables, and meats stay fresh and safe to eat for as long as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best practices for storing fruits and vegetables to maintain freshness?
The best practices for storing fruits and vegetables include keeping them in a cool and dry place, away from direct sunlight. You should also separate fruits and vegetables that produce ethylene gas, such as apples and bananas, from those that are sensitive to it, such as leafy greens and berries. Additionally, it is important to store fruits and vegetables in breathable containers or bags to prevent moisture buildup.
How should fruits and vegetables be organized in the refrigerator?
To organize fruits and vegetables in the refrigerator, you should store them in separate drawers or compartments. This will help to maintain proper humidity levels and prevent cross-contamination. You should also keep fruits and vegetables that produce ethylene gas, such as apples and avocados, away from those that are sensitive to it, such as leafy greens and broccoli.
What containers can extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables?
Containers that can extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables include those that are breathable, such as paper bags and mesh bags. These containers allow for proper air circulation and prevent moisture buildup. You can also use airtight containers for some fruits and vegetables, such as berries and chopped vegetables, to prevent them from drying out.
Is it better to store fruits on the countertop or in the refrigerator?
It depends on the type of fruit. Some fruits, such as bananas and citrus fruits, can be stored on the countertop at room temperature. Other fruits, such as berries and grapes, should be stored in the refrigerator to maintain freshness. It is important to check the specific storage requirements for each type of fruit.
What are the guidelines for using plastic bags in fruit and vegetable storage?
When using plastic bags for fruit and vegetable storage, it is important to choose bags that are breathable to prevent moisture buildup. You should also avoid overcrowding the bags, as this can lead to bruising and spoilage. Additionally, you should make sure to remove any excess air from the bags to prevent oxidation.
How does the order of food placement in storage affect its longevity?
The order of food placement in storage can affect its longevity. It is important to store fruits and vegetables separately to prevent cross-contamination and to keep fruits and vegetables that produce ethylene gas away from those that are sensitive to it. Additionally, you should store meats and dairy products on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator to prevent any potential drips or spills from contaminating other foods.