Probiotics and Gut Health: Importance of Probiotics for Digestion
Probiotics have become increasingly popular in recent years as more people recognize the importance of gut health for overall well-being. These live microorganisms, often referred to as “good” or “beneficial” bacteria, play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. They are naturally present in the body, particularly in the intestines, but can also be consumed through certain foods and supplements. This article explores the significance of probiotics for digestion, the benefits they offer, and how to incorporate them into your diet.
Understanding Probiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial to our health, especially the digestive system. The human gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota. This complex community includes both beneficial and harmful bacteria. A balanced microbiota is essential for optimal digestive function, nutrient absorption, and immune response.
Types of Probiotics
There are many different strains of probiotics, each with its unique benefits. The most common types of probiotics belong to the genera Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, with various species within these genera providing specific health benefits.
- Lactobacillus: This is one of the most common probiotic genera, found in yogurt and other fermented foods. Lactobacillus species help break down lactose, the sugar in milk, and are beneficial for those who are lactose intolerant. They also contribute to maintaining a balanced pH level in the gut.
- Bifidobacterium: These probiotics are also commonly found in dairy products and fermented foods. They are known for their ability to support the immune system and improve digestion by breaking down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Saccharomyces boulardii: This probiotic yeast is beneficial for treating and preventing diarrhea. It helps restore the natural flora in the intestines, especially after antibiotic use.
Benefits of Probiotics for Gut Health
The benefits of probiotics extend beyond digestion. They play a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut environment, which is essential for overall health. Here are some key benefits of probiotics:
1. Enhancing Digestive Health
Probiotics aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients. They help digest food, produce vitamins, and break down toxins. A healthy balance of gut bacteria can prevent issues such as bloating, gas, and constipation. Probiotics also play a crucial role in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which provide energy to colon cells and help maintain a healthy gut lining.
2. Boosting the Immune System
The gut is a major component of the immune system. Probiotics help stimulate the production of antibodies and immune cells, such as lymphocytes and dendritic cells. They also enhance the gut’s barrier function, preventing harmful bacteria and pathogens from entering the bloodstream. By maintaining a balanced gut microbiota, probiotics contribute to a more robust immune response.
3. Preventing and Treating Diarrhea
Probiotics are effective in preventing and treating various types of diarrhea, including antibiotic-associated diarrhea, infectious diarrhea, and traveler’s diarrhea. Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of gut bacteria, leading to diarrhea. Probiotics help restore this balance by replenishing beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
4. Alleviating Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a common digestive disorder characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and irregular bowel movements. Probiotics have been shown to alleviate these symptoms by promoting a healthy balance of gut bacteria and reducing inflammation. Specific strains, such as Bifidobacterium infantis, have been particularly effective in managing IBS symptoms.
5. Supporting Mental Health
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network that links the gut and the brain. Probiotics play a role in this connection by influencing the production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine. Studies have shown that a healthy gut microbiota can positively impact mood and mental health, potentially reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
6. Improving Skin Health
The benefits of probiotics are not limited to internal health. They can also improve skin conditions such as eczema, acne, and rosacea. By reducing inflammation and modulating the immune response, probiotics can promote clearer and healthier skin.
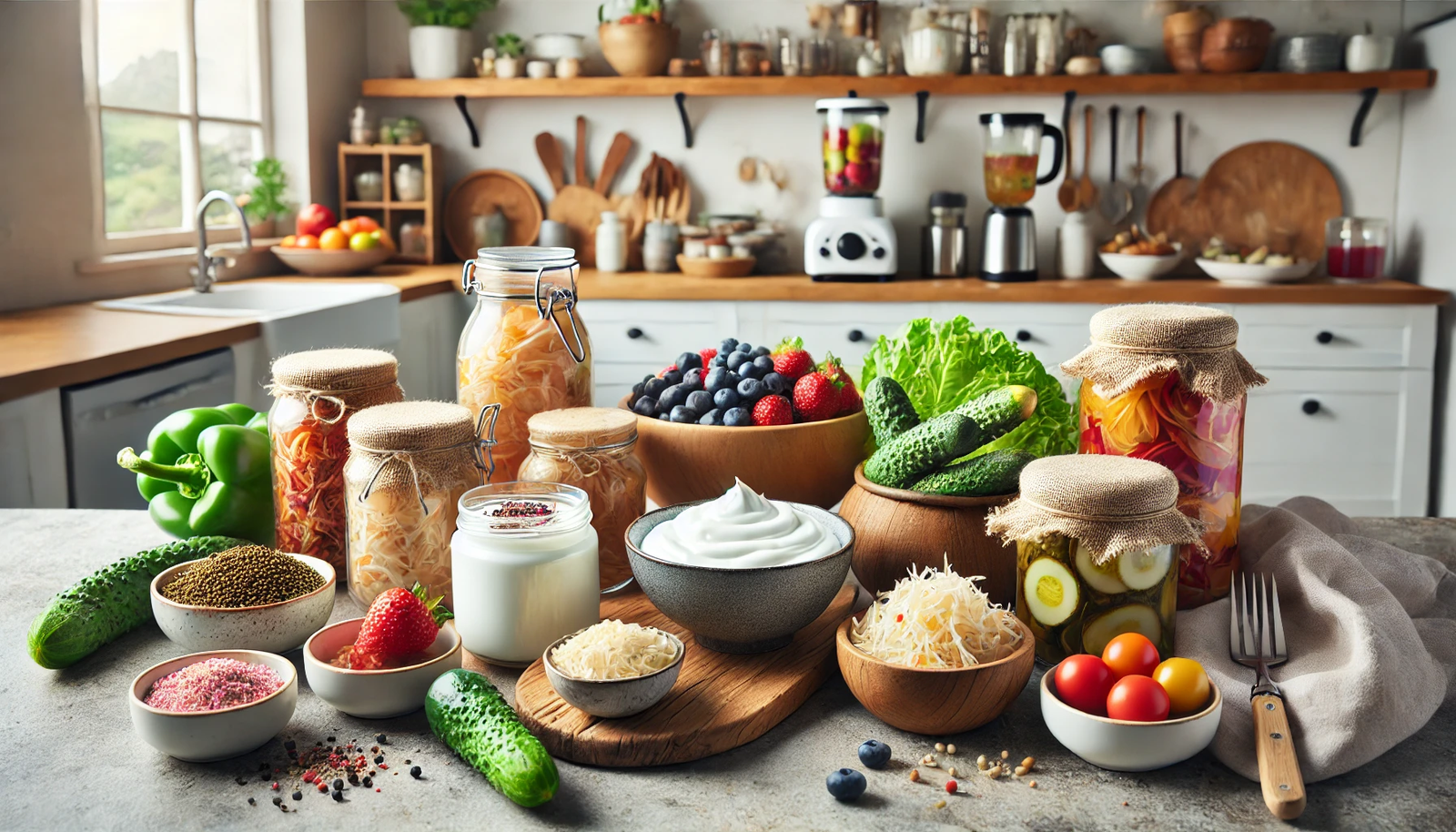
Sources of Probiotics
Probiotics can be consumed through various foods and supplements. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet is a natural way to boost your gut health. Here are some common sources of probiotics:
1. Yogurt
Yogurt is one of the most popular sources of probiotics. It is made by fermenting milk with live cultures of beneficial bacteria, typically Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. When choosing yogurt, opt for products labeled with “live and active cultures” to ensure they contain viable probiotics.
2. Kefir
Kefir is a fermented milk drink that contains a diverse range of probiotic strains. It is similar to yogurt but has a thinner consistency and a slightly tangy taste. Kefir can be made from cow, goat, or sheep milk, and non-dairy alternatives are also available.
3. Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is fermented cabbage rich in probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus species. The fermentation process not only enhances its nutritional value but also imparts a tangy flavor. Sauerkraut can be enjoyed as a side dish, in sandwiches, or as a topping for salads.
4. Kimchi
Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, primarily napa cabbage and radishes. It is seasoned with spices and other ingredients like garlic, ginger, and chili peppers. Kimchi is a rich source of probiotics and is known for its spicy and tangy flavor.
5. Miso
Miso is a traditional Japanese paste made from fermented soybeans. It is commonly used in soups, marinades, and dressings. Miso contains probiotics, particularly beneficial for digestive health, and adds a savory, umami flavor to dishes.
6. Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea beverage that contains probiotics, along with other beneficial compounds like organic acids and antioxidants. It has a fizzy texture and a tangy taste. Kombucha can be found in various flavors and is a popular alternative to sugary sodas.
7. Pickles
Fermented pickles, such as dill pickles, are another source of probiotics. It’s important to note that not all pickles contain live probiotics; only those fermented in a brine solution (water and salt) without vinegar contain beneficial bacteria.
Probiotic Supplements
In addition to foods, probiotics are available in supplement form. These supplements can be particularly useful for individuals who have difficulty incorporating probiotic-rich foods into their diet or require a specific probiotic strain for health reasons.
Choosing a Probiotic Supplement
When selecting a probiotic supplement, consider the following factors:
- Strain Specificity: Different probiotic strains offer various health benefits. Choose a supplement with strains that target your specific health needs.
- Colony Forming Units (CFUs): The CFU count indicates the number of live microorganisms in each dose. A higher CFU count may be beneficial for certain conditions, but it’s important to follow the recommended dosage.
- Quality and Shelf Stability: Look for supplements from reputable brands that guarantee the viability of the probiotics through the expiration date. Some probiotics require refrigeration, while others are shelf-stable.
When to Take Probiotics
Probiotics can be taken at any time of day, but taking them with meals may enhance their survival through the acidic environment of the stomach. Consistency is key, so choose a time that works best for your daily routine and stick with it.
How to Incorporate Probiotics into Your Diet
Incorporating probiotics into your diet can be simple and delicious. Here are some tips to help you get started:
Start with Probiotic-Rich Foods
Begin by adding probiotic-rich foods to your meals and snacks. Enjoy yogurt or kefir for breakfast, add sauerkraut or kimchi to sandwiches and salads, and sip on kombucha throughout the day.
Combine with Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial bacteria in the gut. Combining probiotics with prebiotic-rich foods, such as garlic, onions, bananas, and whole grains, can enhance their effectiveness. This combination is known as synbiotics.
Experiment with Fermented Foods
Explore different types of fermented foods from various cuisines. From miso soup to tempeh and natto, there are many options to choose from. Experimenting with new flavors and dishes can make incorporating probiotics into your diet more enjoyable.
Use Probiotics in Cooking
You can use probiotic-rich ingredients in your cooking. For example, add a spoonful of miso to soups or dressings, or use yogurt as a base for smoothies, marinades, and sauces. Just be mindful of not exposing probiotics to excessive heat, as it can kill the beneficial bacteria.
Conclusion
Probiotics play a crucial role in maintaining gut health and supporting overall well-being. These beneficial microorganisms aid in digestion, enhance the immune system, and contribute to various other health benefits. By incorporating probiotic-rich foods and supplements into your diet, you can promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria and improve your digestive health. Whether you prefer yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, or supplements, there are many ways to enjoy the benefits of probiotics. As always, consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
FAQs
What are probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often referred to as “good” or “beneficial” bacteria, that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They are commonly found in fermented foods and supplements.
How do probiotics benefit the digestive system?
Probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, aid in the digestion and absorption of nutrients, produce essential vitamins, and support the immune system. They can also help alleviate digestive issues like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Can probiotics help with weight loss?
Some studies suggest that probiotics may aid in weight loss and weight management by influencing gut bacteria composition, reducing inflammation, and regulating appetite. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of probiotics on weight loss.
Are there any side effects of taking probiotics?
Probiotics are generally safe for most people, but some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as gas, bloating, or digestive discomfort, especially when first starting. These symptoms typically subside as the body adjusts. However, individuals with compromised immune systems or serious health conditions should consult a healthcare professional before taking probiotics.
Can I get enough probiotics from food alone?
While it is possible to get a sufficient amount of probiotics from food, supplements can be a convenient option for those who have specific health needs or difficulty incorporating probiotic-rich foods into their diet. A combination of food and supplements can help ensure a consistent intake of probiotics.
How do I know if I need probiotics?
Probiotics can be beneficial for most people, but certain situations may increase the need for them, such as after antibiotic use, during times of stress, or when experiencing digestive issues. If you’re considering probiotics for specific health concerns, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.